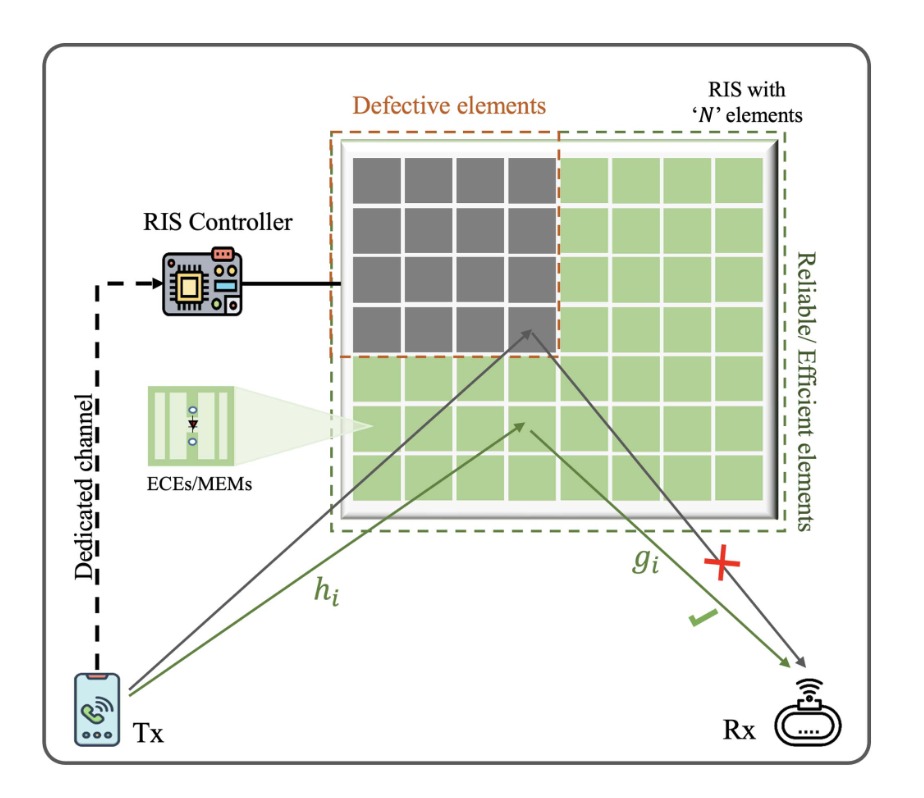
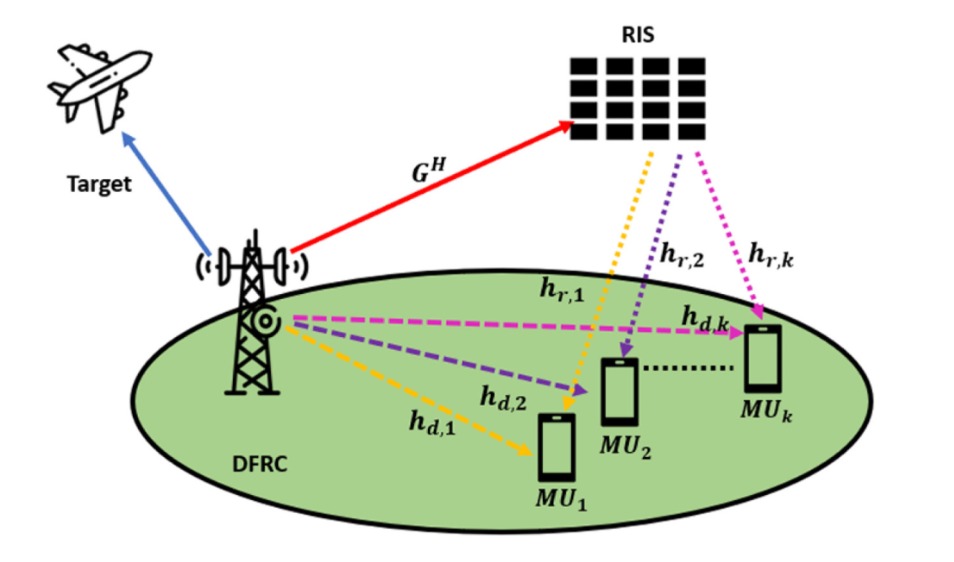
Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA)
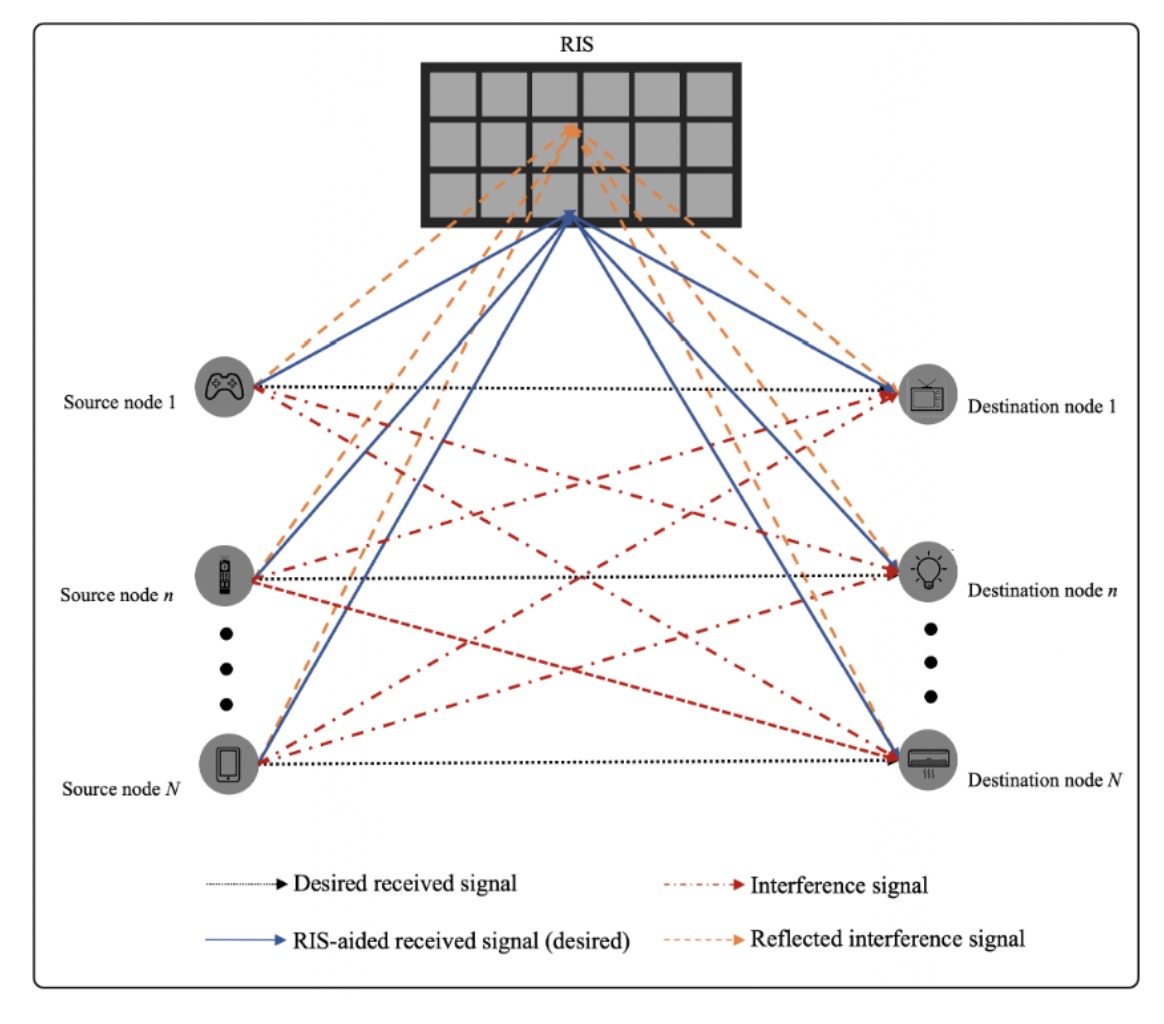
NOMA allows multiple users to share the same time–frequency resource via power-domain superposition and successive interference cancellation (SIC). While this improves spectral efficiency, it also introduces additional co-channel interference, especially in ultra-dense and massive-MIMO deployments. Our work revisits resource management (power control, user clustering, SIC ordering) and interference mitigation, and develops robust beamforming/precoding strategies for practical, imperfect-CSI settings so that NOMA can be fully and reliably utilized.